- Automation
- Home
- /
- Learning Hub
- /
- What Is Quality Assurance
- -
- May 30 2023
What Is QA? A Beginner Guide to Quality Assurance
Explore Quality Assurance in the software testing and development process, its challenges with strategies to overcome, and the benefits of implementing the QA process.
Total Chapters (8)
Chapter 1 : What Is QA? A Beginner Guide to Quality Assurance
OVERVIEW
Quality Assurance (QA) is an essential process focused on creating standards and procedures to ensure the reliability of a software product or service during development. The main aim is to prevent quality issues by establishing the right methodology and standards.
It is crucial to securing business success by consistently maintaining the desired product quality. Through various measures, QA improves customer satisfaction, increases sales, and builds a positive brand image.
In this tutorial, we will delve into the terms of quality, explore the concept of assurance, define quality assurance, and understand the necessity of implementing quality assurance in testing. We will also discuss relevant tools, challenges, and more.
So let's get started.
What is Quality?
In simple terms, quality is centered around meeting your customers' needs. When we talk about the "quality of a product or service," it refers to how well it includes features and characteristics that serve the customer's requirements and satisfy their needs.
What is Quality Control?
Quality control, often referred to as QC, is the systematic process employed by businesses to guarantee that a product or service aligns with predetermined quality standards and fulfills the expectations of customers or clients.
Implementing quality control necessitates an environment within the business where employees and management are committed to achieving excellence.
This involves thorough training, establishing benchmarks to assess the quality of products or services, and conducting tests to identify any notable deviations in quality.
This gave you an overview of what quality and quality control is. Let us look into what quality assurance is in the next section.
What is Quality Assurance (QA)?
Software Quality Assurance (SQA) is a continuous process used by IT companies to ensure their products meet high standards and follow industry rules.
SQA ensures everyone involved in software development does their job well so the final product meets the set standards instead of checking quality only at the end.
It happens alongside development. This helps identify and fix issues early in the software development process. Delivering a quality product builds a good brand image, keeps customers happy, and grows the business.
Quality assurance ensures the process is constructed and followed to provide a high-quality product. This QA involves the activities that help prevent defects and deviations from standards, promoting consistent and effective testing practices across the entire development life cycle.
Some of the activities are mentioned below.
- Setting up procedures and standards
- Adhering to standards
- Prompt monitoring and reporting
- Managing the test environment
- Offering recommendations and feedback
Quality Assurance (QA) establishes effective and consistent testing practices by defining procedures and standards. This involves creating testing templates, specifying testing methods, and setting various criteria for testing.
QA ensures the testing team adheres to established procedures and standards, preventing unnoticed deviations. This consistency improves with the efficient implementation of QA procedures.
Regarding monitoring and reporting, QA oversees the testing process, identifying and reporting problems promptly. This includes recognizing defects and tracking their resolution progress.
The QA is responsible for managing it and ensuring its proper setup. It involves configuring test environments, collecting test data, providing tool availability, and ensuring prompt functionality.
QA provides recommendations to the development team to enhance software quality. This encompasses identifying areas for improvement in testing and suggesting modifications to the software development or design process.
Difference between Quality Control and Quality Assurance
| Quality Control | Quality Assurance |
|---|---|
| Focuses on quality requirements, ensuring that a part meets specifications. | Focuses on all the activities and procedures that showcase the satisfaction of quality standards and requirements. |
| Specific and detailed, targeting individual components or processes. | It encompasses a broader scope, including all activities and departments, ensuring overall quality. |
| Often involves inspection and testing of products during or after production. | Involves comprehensive programs and departments, assuring various stakeholders that products meet quality and safety standards. |
| Reactive approach, identifying and rectifying defects in the finished product. | Proactive approach, implementing processes to prevent defects and ensure consistent quality throughout production. |
| Typically, part of the production phase is ensuring compliance with set standards. | Extends beyond production, covering the entire product development life cycle. |
| Emphasizes finding and fixing issues to meet specific criteria. | Emphasizes a holistic approach, demonstrating overall adherence to quality requirements. |
Key Principles of Quality Assurance
Quality Assurance in any organization is guided by fundamental principles, forming a roadmap to achieve customer-centric excellence and a continuous feedback-based improvement cycle. Here are some core principles.
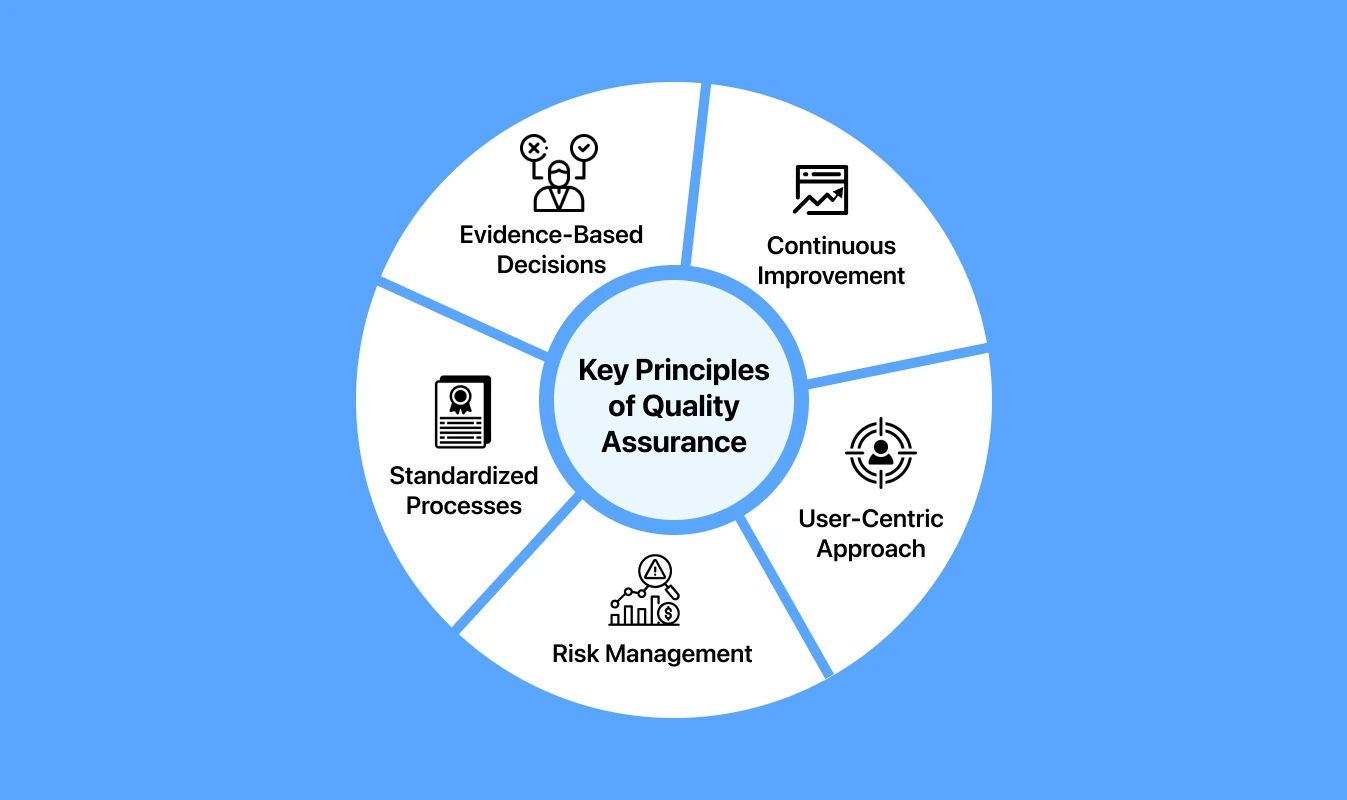
- Continuous Improvement
- User-Centric Approach
- Risk Management
- Standardized Processes
- Evidence-Based Decisions
Emphasizes the ongoing evaluation of existing processes and the implementation of necessary changes to enhance efficiency and effectiveness consistently.
Places the customer at the core of Quality Assurance, involving a deep understanding of their requirements, expectations, and preferences. This approach tailors strategies to deliver satisfying experiences and products.
Essential for assuring quality involves identifying, assessing, and mitigating risks. Anticipating potential issues and establishing contingency plans foster a proactive approach to prevent deviations from planned outcomes.
Advocates for standardizing procedures and protocols across various processes. This principle promotes clear expectations, minimizes errors, and enhances the quality of deliverables.
Encourages organizations to base decisions on reliable information, ensuring that choices are grounded in evidence. This approach leads to effective and impactful enhancements in quality.
Along with some core key principles, there are some components of quality assurance. Let's explore the component in more detail in the following section.
Quality Assurance Components
Quality Assurance comprises eight key components to ensure the smooth functioning of development and testing. These elements cover organized activities designed to ensure consistency, prevent defects, and enhance the overall quality of the service or product. Let's explore them.
- Quality Planning
- Quality Control
- Documentation
- Competence and Training
- Collective and Preventive Steps
- Review and Auditing
- Consistent and continuous improvement
- QA Metrics and Reporting
It involves defining necessary quality standards and creating a full-fledged plan to meet them successfully. Professionals involved identify customer requirements, set objectives, and determine the required processes and resources to achieve them.
QC monitors and inspects the systems during delivery or production to identify deviations and defects from quality standards. This process includes inspection and testing of the product, along with data analysis.
The Documentation component of the QA process involves jotting down clear work instructions, creating SOPs, and other relevant parameters that require serious implementation. Process documentation involves outlining each step and all quality criteria.
Competence and training include thoroughly checking that every team member involved in production and delivery is competent and sufficiently trained to maintain set quality. QA programs also include training activities to help employees reach this level of knowledge and skill and help them understand their duties.
In case of a deviation from preset quality standards or a defect, the QA team is responsible for taking preventive and corrective actions to avoid this behavior in the future. This component also involves addressing the root cause of a problem after a thorough investigation.
Regular reviews and audits can assess how effective a company’s QA processes are and recognize areas of improvement. Internal and external audits are necessary to ensure compliance with regulatory requirements and quality standards.
QA professionals collect and analyze data, solicit customer feedback, and implement performance-enhancing changes. This component reinforces that Quality Assurance is not just a one-time practice, but instead, it's a continuous process of consistent improvement.
As we already know, KPIs and QA metrics accurately measure the effectiveness of QA efforts. When the professionals regularly report quality metrics, it offers visibility into how the product performs and highlights improvement areas.
Note : Improve your software quality by eliminating bugs and accurately managing QA metrics. Try LambdaTest Now!
Now that we know the key principles and core components of quality assurance, in the following section, let us learn more about how you need to carry out quality assurance.
How to Carry Out Quality Assurance?
Quality Assurance steps involve various activities designed to prevent errors and effects. These steps verify whether a product or service meets customer expectations and needs. There is a detailed breakdown of how to carry out QA.
- Define requirements and standards.
- Develop a QA plan.
- Create test cases.
- Execute and pinpoint issues.
- Correcting defects
- Retest and report
The first step to great Quality Assurance is to define the requirements and standards that software, products, or services must meet. It involves conducting a detailed review of regulatory requirements, customer expectations, industry standards, and other relevant factors.
Once you have found all the QA requirements, it's time to develop a killer QA plan. Ideally, this plan should outline specific activities that prove how the product or service under test meets the defined standards, regulations, and requirements.
After developing a robust QA plan, it's time to identify key functionalities of the software and design test cases. to verify whether those functionalities are working as per designated expectations.
Whether manual testing, automated testing, or a combination of both, this step is about executing the above test cases and identifying issues and effects. Document them and track them to ensure prompt addressing and resolution.
Once you have identified all the bugs, it's time to correct them. It might involve fixing configuration issues, debugging code, or modifying the entire product or service.
After you have fixed all the bugs, it's time to Retest the software product to ensure the success of the changes and whether it meets the mandatory quality standards. Document these results and create a report summarizing test results, analytics, issues, and improvement recommendations.
We have already learned about the differences in quality assurance, how to carry out quality assurance, and its key principles. Let us know about the primary quality assurance process.
Main Stages in the QA Process
A QA process is a way to check if a product meets what is expected. Performing software testing might differ based on the organization and its needs, but the steps below are crucial to follow.
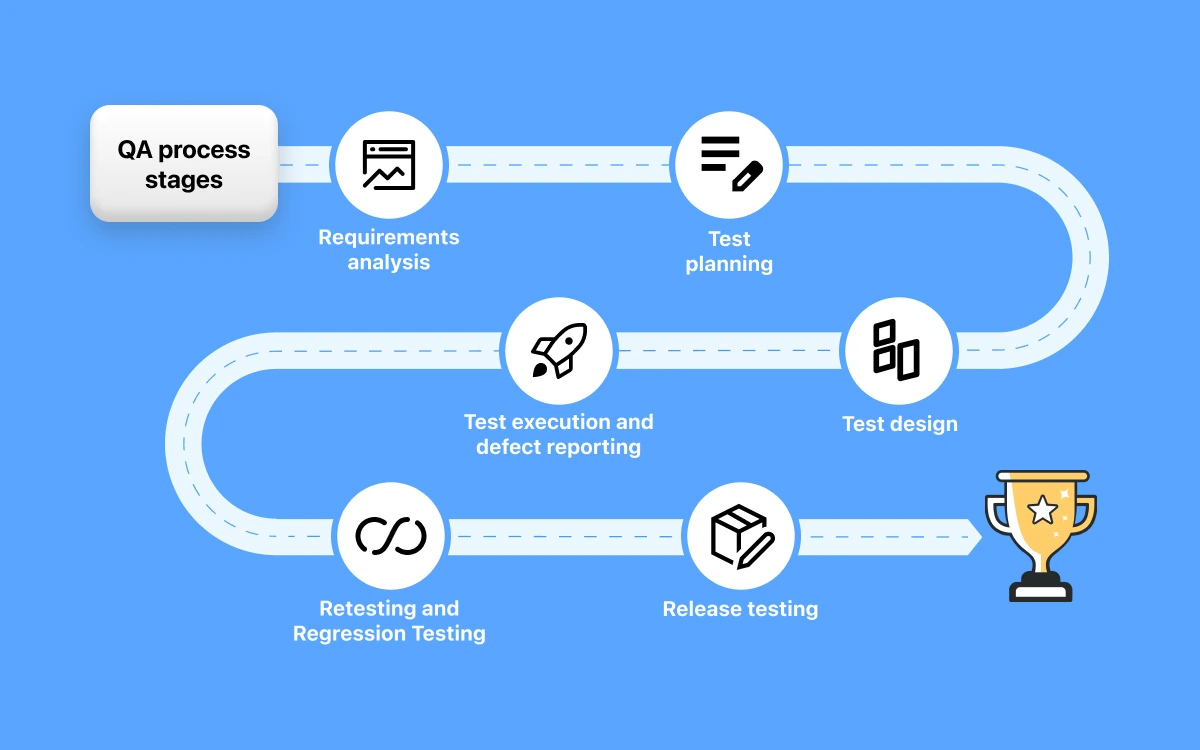
- Requirement Analysis
- Test Planning
- Test Design
- Test Execution and Defect Reporting
- Retesting and Regression Testing
- Release Testing
Before starting any work, it's crucial to understand what's needed. The QA team carefully looks at all the software requirements, ensuring they are clear, complete, and ready for testing. It helps prevent problems down the road and guides the upcoming testing plans.
Building on the requirements, the QA team makes a plan for testing. This plan includes the scope of testing, budget, and deadlines. It also outlines the types of tests needed, reporting procedures, and how to track and handle any issues found during testing.
With the plan in place, the QA professionals create detailed test cases covering all the requirements. These test cases outline the conditions, data, and steps needed to check specific functions of the software. Test engineers may experiment to find the best ways to design tests. They also prepare a testing environment that closely resembles the actual production setup.
The testing begins with unit tests. Manual testers follow the designed test cases, reporting any issues they discover. Automation engineers use scripts to run automated tests. Defects found are documented in a tracking system.
After fixing any identified issues, the team retests the affected areas to ensure the problems are solved without causing new ones. They also perform regression testing to check that the changes haven't negatively impacted existing functionality.
When the development team announces a new release, the QA team checks for changes that might affect the software's performance. They conduct smoke testing to ensure the release is stable. If everything looks good, they run specific test suites, and the results are documented and shared.
Now that you know what QA is all about and its process, let us look into the benefits of implementing the QA process below.
Why Should QA Processes Be Implemented?
Implementing a robust quality assurance process is essential for various compelling reasons. Let's explore the advantages of implementing a QA process and the risks of neglecting it.
Risks of Not Implementing a Quality Assurance Process
The quality assurance process is a systematic undertaking by software testers to evaluate whether a product aligns with defined quality standards. Overlooking this essential quality assurance process can impact product quality.
- Dissatisfied Users: Software defects can drive away users, decreasing customer loyalty and dissatisfaction.
- Reputation Damage: Negative reviews due to poor quality can harm your reputation and impact your brand image adversely.
- Trust Issues: Subpar product quality erodes trust among users and potential investors, posing challenges for the business.
- Sales Impact: Insufficient product quality undermines sales efforts, causing new customers to leave when unmet needs are met.
- Compatibility Problems: Introducing updates without proper quality assurance may cause existing features to malfunction.
- Distraction and Delays: Quality issues divert the team's focus, resulting in developers spending time fixing bugs instead of implementing new features.
- Deployment Challenges: Quality issues can hinder the smooth deployment of new features, as the development team must address existing defects first.
Prioritizing the QA process is crucial to mitigate these risks, ensuring a high-quality product that meets user expectations and drives customer satisfaction.
Benefits of Implementing a QA Process
Conversely, a well-organized quality assurance process substantially benefits your business, enhancing product quality and customer satisfaction. These benefits include:
- Time Dedication: Your team can dedicate more time to enhancing the product and introducing new features.
- Reduced User Complaints: Satisfied users are less likely to raise complaints, reducing the workload on the customer support team.
- Higher Product Quality: Improved product quality reduces concerns about potential failures, enhancing overall reliability.
- Cost Minimization: Proper quality assurance helps minimize project costs, as preventing defects is more cost-effective than fixing them later.
In summary, implementing an effective quality assurance process is a strategic investment that safeguards against risks and elevates your product's overall quality and success.
Types of Quality Assurance Testing (Manual & Automation)
Quality assurance testing involves using different methods to check if software and apps work well. These testing techniques find problems, ensure the software follows the rules, and improve its quality. Now, let's explore the two main types of quality assurance testing.
Manual Testing
Manual testing involves human interaction with the software to validate its functionality and assess its usability. This approach enables testers to mimic real-world scenarios and analyze software from an end-user’s perspective.
Manual testing comes in various forms, each with its unique approach for different purposes and types of software. Here are some of the most frequently used testing types.
Functional testing
This testing focuses on the functional requirements of an application, testing various actions and system functions. It involves giving input to the system and comparing the actual output with the expected one. Test cases are created based on the software and customer
Functional testing typically performs the following checks:
- Testers must understand how the application functions.
- Always use the appropriate set of data for testing
- The application's functional requirements should match the test data used for output.
- Ensure that all test scenarios are covered.
- Record and review the results against the expected output.
Regression testing
This testing is a part of functional testing performed to check if the software still works as intended after developers make changes or fixes. When developers enhance the software, it could unintentionally affect other application parts. Regression testing ensures new changes don't harm existing features or introduce new bugs. This type of testing can be done using automation tools like Selenium. It involves re-running a set of test cases that have previously passed to ensure everything still works correctly.
Usability testing
In simple terms, the tester checks how easy it is for users to use the application. It falls under black box testing, where the application is tested to ensure users can easily interact with its interface. Testing has three main aspects: convenience, usability, and learning ability.
Usability testing aims to ensure the quality and user-friendliness of the application. To explain, let's take the example of a gaming app. Usability testing for this app checks if it can be operated with both hands, examines the background color, looks at the vertical scroll, and more.
Different types of usability testing include:
- Cross Browser Testing: This involves testing the application on other browsers, operating systems, and mobile devices to ensure it works well everywhere.
- Accessibility Testing: This type of testing checks how accessible the software is for people with impairments. For instance, it looks at font size and color to accommodate visually impaired users and those with color blindness.
- Exploratory Testing: This more informal type of testing aims to identify and address existing defects. It relies on the tester's business domain knowledge to validate the application.
Acceptance testing
After finishing unit, integration, and system testing in software application testing, the next stage guarantees the application's quality. The quality assurance team conducts tests based on predefined cases and scenarios to assess the quality. The quality assurance team examines the entire system's design and internal functions during acceptance testing. This step is essential in testing software apps because it considers the contractual and legal requirements set by the clients.
Manual testing becomes challenging as software complexity increases, which leads to a growing number of testing scenarios, and human errors in developing and testing also rise. Additionally, conducting manual tests across various browsers and platforms can be time consuming and requires more human resources to manage the testing process.
Automation testing can be beneficial in overcoming these manual testing challenges.
Automation testing
Automated testing uses automation testing tools and frameworks to test cases, compare expected and actual results, and detect defects. It provides efficiency, repeatability, and quick feedback on software quality. Various types of automated testing include
Unit testing
This type of testing is performed on specific components of the software applications' parts to ensure they work correctly. It is done by testing individual units or sections of the source code. Unit testing happens early in the software development, and developers carry it out.
There are two main types of unit testing:
- White Box Testing: You check the internal structure of the code. It helps find any mistakes in how the application is designed. Data flow testing, path testing, decision coverage, and control flow testing are used here.
- Gorilla Testing: In this type of testing, inputs are repeatedly applied to the module to ensure it works well and the application doesn't crash. It tests every part of the code using random inputs. It checks how robust the application is, and because it involves every module, it's also called fault tolerance or torture testing.
Integration testing
This testing type brings units or software application modules together to check how the system works. In simple terms, it involves combining and testing two or more modules of an application together.
Integration testing aims to discover bugs in how modules connect, how data moves, and how they interact. Testers explore how different units work together and produce results in various situations.
It helps identify errors related to performance, requirements, and functionality. While unit testing checks individual units to ensure they perform as expected, integration testing assesses how well these units work when combined.
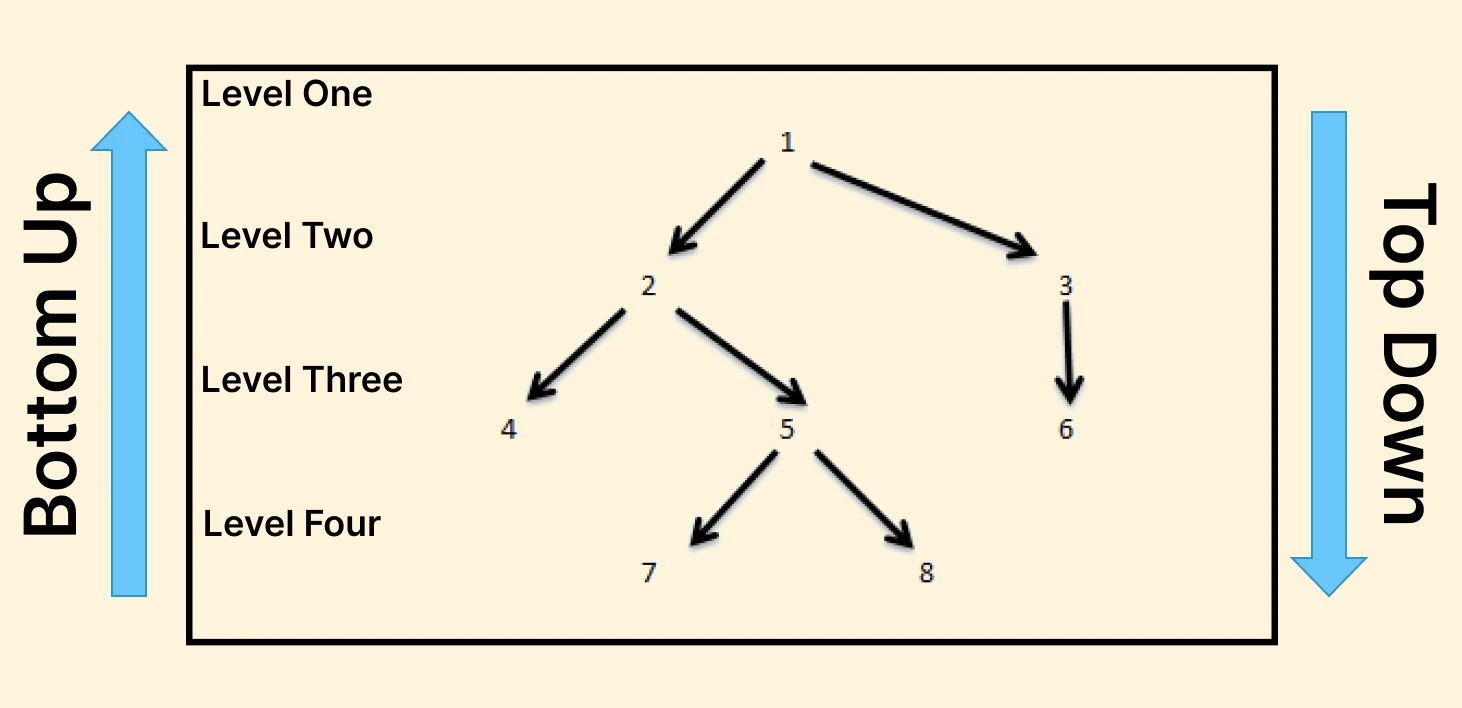
There are three main types of integration testing:
- Big Bang: This method combines all application modules to form a complete system, followed by bug testing.
- Top-Down Approach: Initially, the top-level module is tested, then sub-modules are added and tested.
- Bottom-Up Approach: Unlike the top-down approach, this testing starts by testing the lowermost modules. Then, a stepwise approach is used to add and test higher-level modules.
Performance testing
This type of testing checks if a software application meets its performance goals, like how fast it responds and how much work it can handle. This type of testing uses tools like LoadRunner, JMeter, Loader, and others.
There are different types of performance testing:
- Load Testing: This checks if the software stays stable when it handles the expected number of users. For example, if your app handles 250 users at once with a response time of three seconds, load testing checks if it still works well with 250 or fewer users.
- Stress Testing: This checks how the application holds up under more stress than designed. For instance, if the app is made for 5000 users with a response time of five seconds, stress testing checks how it performs with 5000 or more users.
- Scalability Testing: This checks if the application can handle more load than it's designed for and finds out where it might crash. For example, suppose an app handles 3000 users with a response time of five seconds. In that case, scalability testing checks how the application handles more than 3000 users, gradually increasing the load to find the breaking point.
- Flood Testing: This tests a database's stability and response time by transferring a large set of data. It checks how well the database can manage the data.
- Endurance Testing: This ensures the application can handle a continuous load over time. It checks if the application works properly for an extended period.
Security testing
Software testing looks into security to uncover an application's risks, threats, and vulnerabilities. The goal is to prevent attacks and find weaknesses in the software system. It focuses on two essential aspects: authentication and authorization, making the application secure for handling confidential information.
Security testing also examines how the software behaves during hacker attacks and how it can maintain data security in such situations.
Different types of security testing exist
- Penetration Testing: This evaluates the system for vulnerabilities against external hacking attempts. Authorized cyberattacks are conducted to understand the system's limits in terms of security. It involves SQL injection, Privilege Elevation, session expiry, and URL manipulation.
- Vulnerability Scanning: Automated software scans the system for vulnerability signatures.
- Security Auditing: This involves an internal inspection of applications and the operating system for security limitations. It also includes a line-by-line code inspection.
- Security Scanning: This is done to find weaknesses in the system and network and provide solutions to reduce associated risks.
- Ethical Hacking: This involves hacking. In that case, an organization's software system with the primary intention of uncovering security flaws.
- Portability Testing: This type of testing checks how changes in the environment affect the software's performance. For instance, it assesses how the software works in different versions of operating systems or web browsers.
Automated testing provides benefits such as faster test execution, managing large test suites, and the ability to repeat test cases. It is especially advantageous for tasks like regression testing and situations that demand comprehensive test coverage.
By combining manual and automated testing methods, quality assurance teams can thoroughly check the software, find problems, and ensure its quality and reliability. Choosing the right testing tools and methods depends on project needs, deadlines, and available resources. Using a balanced approach to testing makes quality assurance efforts more effective and efficient, leading to top-notch software that meets user expectations.
Now that we are aware of the types of testing, let us look into the tools that can help us maintain the quality when performing testing and that makes the tester's life easy.
Tools Required for Quality Assurance Testing
Software development teams use quality assurance testing tools to guarantee that their releases align with project requirements, provide an excellent user experience, and have minimal bugs and defects.
LambdaTest
LambdaTest is an AI-powered test orchestration and execution platform that lets you run manual and automated tests at scale with over 3000+ real devices, browsers, and OS combinations.
This platform allows you to conduct QA testing on various browsers and operating systems without complex setups. LambdaTest can improve efficiency by automating repetitive tasks and saving time and human resources. Get started with your automation testing journey; explore this video tutorial to learn how to leverage LambdaTest to make your automation easy.
Subscribe to the LambdaTest YouTube Channel and stay updated with the latest tutorials around Selenium testing, Cypress testing, and more tutorials.
Some of the key features of LambdaTest are mentioned below.
- LambdaTest offers access to a diverse range of 3000+ browsers and operating systems, enabling comprehensive testing across various devices.
- It supports parallel testing, allowing the simultaneous execution of multiple tests on different browsers and devices, optimizing testing efficiency.
- It smoothly integrates with leading test automation frameworks, facilitating a quick and straightforward start to application testing.
- Advanced debugging tools, including video recording, network, and console logs, are provided for swift bug identification and resolution.
- LambdaTest features a scalable mobile device lab with thousands of real Android and iOS devices, enhancing mobile testing capabilities.
Selenium
This is an open-source automated testing tool that enables users to create and run tests for web applications. With its compatibility across various programming languages, Selenium facilitates testing applications on multiple platforms. This tool is particularly advantageous for teams seeking a quality assurance testing solution that is both adaptable and customizable.
Some of the key features of Selenium are mentioned below.
- It works smoothly with web browsers, including Chrome, Firefox, Safari, and Edge.
- Supports multiple programming languages like Java, Python, C#, Ruby, and more.
- Integrates with frameworks such as JUnit, TestNG, and others.
- Allows for parallel testing, enabling the concurrent execution of multiple tests.
- Includes a recording and playback feature through Selenium IDE for efficient test automation.
- Highly adaptable, offering flexibility to add plugins and extensions as needed.
- Benefits from a vibrant and engaged user and developer community, making problem-solving and support easily accessible.
To know more about Selenium and how you can leverage the automation testing process with Selenium suites with various languages like Java, Python, and more with advanced use cases, follow this complete guide on Selenium WebDriver and enhance your testing experience.
Appium
This is an open-source and widely recognized tool. It tests native, hybrid, and mobile web applications and can drive Android, iOS, and Windows apps through the WebDriver protocol. The fundamental concept underlying Appium is that testing a native app should not necessitate an SDK or app recompilation. Instead, the focus is on leveraging your preferred test frameworks, methodologies, and tools to conduct effective mobile app testing using Appium.
Some of the key features of Appium are mentioned below.
- It offers flexibility to test mobile applications in any programming language and with any test framework, providing full access to back-end APIs.
- It stands out as one of the top test automation frameworks due to its cross-platform compatibility. It allows the same API to run tests on multiple platforms and operating systems, enhancing code reusability.
- With Appium, testers are not required to recompile the mobile application each time they run automation tests, streamlining the testing process.
Jenkins
This Continuous Integration (CI) orchestration tool boasts an extensive plugin and helps smooth integration with various test automation tools and frameworks within the test pipeline. It excels by offering plugins designed to execute test suites, compile dashboard results, and furnish comprehensive information on test failures.
Some of the critical features of Jenkins are mentioned below.
- This comes with plugins for test frameworks such as Selenium, Cucumber, Appium, etc. These plugins smoothly integrate into CI pipelines, enabling the automated execution of tests for every build.
- The majority of Jenkins plugins not only execute tests but also summarize the results, presenting them in the form of an HTML page for easy analysis.
- It records test results, presenting them in a trend graph. This visual representation offers valuable insights into the historical performance of tests, aiding in trend analysis.
- Test results are systematically tabulated, and instances of failures are carefully logged alongside the corresponding test results, providing detailed insights into the testing process.
- To gain a comprehensive understanding of Jenkins and its working and integration with your test scripts, watch this dedicated series on Jenkins and make your testing process easy and effective.
JUnit
This is one of the most widely used unit testing frameworks. JUnit 5, developed as an enhancement over its predecessor, JUnit 4. x, represents a comprehensive rewrite. This revamped version offers an adaptable Java testing framework capable of accommodating various testing styles.
JUnit 5 is designed to organize the testing process, simplify parallel testing, and facilitate alternative approaches like property-based testing. A comparative analysis of JUnit 5 versus TestNG reveals the distinct advantages that JUnit 5 provides compared to other Java test automation frameworks.
Some of the key features of JUnit are mentioned below.
- These serve the purpose of labeling test methods, simplifying their identification and execution.
- JUnit provides a robust test runner system supporting parameterized testing. This feature allows the execution of the same test method with various parameters, offering significant utility for testing diverse inputs or scenarios. While some frameworks may also offer parameterized testing, JUnit's implementation is widely recognized and thoroughly documented.
- This functionality aids in organizing or grouping tests, which is particularly useful when intending to execute a collection of related tests together.
TestNG
This is a Versatile and top-tier automation testing tool. The name itself implies "Next Generation" capabilities. Inspired by JUnit, TestNG optimally utilizes annotations (@) to enhance the testing process. Beyond traditional UI testing, TestNG smoothly extends its functionality to encompass end-to-end (E2E) testing and integration testing; this versatility makes TestNG an ideal choice for conducting comprehensive testing scenarios.
For a deeper understanding of this testing framework, consider exploring this tutorial on TestNG.
Some of the key features of TestNG are mentioned below.
- TestNG simplifies the organization of test methods by allowing categorization into groups, facilitating the selection and execution of specific subsets based on criteria like functional areas, priority levels, or environment compatibility.
- Built-in support for parallel test execution maximizes efficiency by running tests concurrently, leveraging multi-core processors.
- Data-driven testing is streamlined with TestNG, enabling test data reading from diverse sources such as XML files, Excel spreadsheets, and databases. This approach enhances test coverage, efficiency, and effectiveness by facilitating easy test generation and running the same tests with multiple data sets.
- The framework incorporates a robust listener mechanism, empowering users to define custom listeners that respond to events during test execution. Custom listeners can be employed for tasks like generating reports, logging, capturing screenshots, and managing test environments.
- TestNG offers the ability to specify dependencies between test methods, ensuring that a test method runs only when specified dependencies pass. This feature is crucial for maintaining the logical execution of test scenarios and upholding test integrity.
Cucumber
Cucumber is a widely used testing tool that supports Behavior Driven Development (BDD). It focuses on creating tests that are easy to understand, regardless of technical knowledge. In BDD, product owners and business analysts lead in writing acceptance tests or test scenarios to simulate system behavior from a business perspective.
This step is crucial for product owners to review before proceeding to code implementation. The combination of Selenium and Cucumber provides a strong framework, making it simple to create functional tests.
Some of the key features of Cucumber are mentioned below.
- Tests can be written in simple language for easy collaboration between technical and non-technical team members.
- Develop modular and easily maintainable test scripts by reusing step definitions across different scenarios.
- Effortlessly integrate Cucumber with CI/CD tools to automate and streamline testing within your development pipeline.
Many automation testing frameworks can help the QA team understand and use them effectively based on their project needs.
Postman
A highly utilized automation testing tool designed explicitly for APIs. Users can author various tests, spanning functional, integration, and regression tests, and seamlessly automate their execution in CI/CD pipelines through the command line.
Some of the key features of Postman are as follows.
- User-friendly interface with readily available code snippets for ease of use.
- Extensive support for various HTML methods, Swagger, and RAML formats.
- Robust support for API schemas, facilitating the generation of collections and API elements.
- Creation of test suites, execution with parameterization, and debugging capabilities.
- Smooth integrations with well-known CI/CD tools.
SoapUI
A free-to-use API testing tool, this software is designed for REST and SOAP web services. It boasts essential functionalities such as automated testing for functions, performance, regression, and security. Users also have the option to explore the enhanced features offered in the commercial version, ReadyAPI (previously known as SoapUI Pro).
Some of the key features of SoapUI are as follows.
- Streamlined test creation through drag-and-drop functionality, even in intricate scenarios.
- Service stimulation to alleviate the effort required for constructing production systems for testing.
- Quick and straightforward reusability of test scripts.
- Expanded protocol support, enhanced capabilities, and seamless integration with CI/CD through ReadyAPI.
TestRail
TestRail offers extensive test case management solutions for software testing, providing a structured approach to enhance organization, productivity, and real-time insights.
Utilized by numerous QA and Development teams, TestRail's web-based platform simplifies software testing processes' organization, tracking, and management. Its user-friendly interface facilitates the creation of test cases, initiation of test runs, and capturing of testing results, and smooth coordination throughout the testing lifecycle.
Some of the key features of TestRail are as follows.
- The user-friendly design simplifies the creation of test cases and the initiation of test runs.
- Track the status of individual tests, milestones, and projects using dashboards and activity reports, providing actionable insights into testing progress.
- Highly adaptable to individual needs, TestRail supports cloud-based and on-premise installations.
- Integrates with leading tools for issue tracking, test automation, and more, including Atlassian Jira, FogBugz, Bugzilla, GitHub, TFS, Gemini, Assembla, BitBucket, Ranorex Studio, and others.
- Enhance productivity through personalized to-do lists, robust filters, and email notifications, ensuring efficient collaboration and task management.
Squish
It is a GUI automation testing tool for various applications, including cross-platform desktop, mobile, embedded, and web applications. It streamlines the verification process for properties, images, complex data, external files, and databases.
Squish lets users record and edit tests using JavaScript, Perl, Python, and Ruby scripting languages. Additionally, it features a comprehensive test development environment built on Eclipse.
Some of the key features of Squish are as follows.
- This tool ensures swift and adaptable GUI automation, allowing customized test run times and early issue detection.
- Guarantees high application quality by seamlessly interacting with user interfaces across various technologies and toolkits.
- It fully uses Behavior-Driven Development (BDD), an advanced testing approach that aligns stakeholders from both business and technical projects to produce top-quality applications.
- Its built-in server securely manages all data related to applications under testing, offering a convenient test suite and IDE tool.
- It excels in test management, supporting various scripts like Python, Ruby, Perl, and TCL.
- This tool automatically records and identifies high-level elements and communications during automation testing.
- Pick and Verification Points tools authenticate test element properties, verify table values, and compare images for robust verification.
- It facilitates distributed batch testing, enabling the creation of script libraries to test specific parts of the entire application.
- It offers a simplified one-click integrated remote control for most targets, seamlessly integrating with tools like ALM, Builds, Project Management, Continuous Integration, and Test Management.
- A multi-user automation tool that generates dependable test scripts, simplifying troubleshooting, maintenance, and test creation.
- Provides a complete testing package with image-based, object-based, and optical character recognition capabilities.
Katalon Studio
Katalon Studio performs end-to-end test automation for web, mobile, and API applications, providing comprehensive capabilities for test generation and execution and fostering team collaboration and feedback. It proves valuable for continuous testing, seamlessly integrating into the ecosystem and transforming automated tests into continuous ones. This tool is an automation solution for testing web, mobile, API, and desktop applications. With flexible automation support, it accommodates projects and teams of any size on a global scale.
Some of Katalon Studio's key features are mentioned below.
- Enhanced testing features include automatic retry for failed tests, smart wait functionality, and self-healing mechanisms to optimize test execution.
- The tool allows the use of reusability by allowing the creation of reusable test objects, keywords, and test cases. It facilitates artifact sharing and adopts the page object model design for better test organization.
- integrates with popular CI/CD and ALM tools like Jira, GitLab, Jenkins, Bitbucket, Azure DevOps, and more. This ensures a smooth workflow within established development pipelines.
- A smart debugging UI and detailed test reporting are provided to troubleshoot failures, quickly enhancing the overall debugging process.
- The tool extends its usability by integrating with popular collaboration tools, contributing to improved test planning and overall team collaboration.
To know more about usability testing and its methods, explore these usability testing methods to leverage your testing approach to make your testing process easy.
Quality Assurance Challenges in Testing
Testing is crucial for delivering quality products to users. However, achieving this goal comes with challenges. Organizations often adopt efficient quality assurance practices to meet client expectations. Many software organizations prefer agile methodology, requiring a highly reliable and spontaneous testing process to meet deadlines. QA testing extends beyond technical aspects. Efficient collaboration among cross-functional teams, clear communication of requirements, and maintaining test data integrity are the most challenging aspects.
Now, let's explore some common challenges testing professionals face in ensuring quality deliverables.
- Incomplete or incorrect Requirements
- Communication Breakdowns
- Limited Resources
- Changing Requirements
- Technical Challenges
- Testing in Production Environments
- Test Automation Challenges
- Balancing Speed and Quality
Sometimes, clients don't communicate their needs during the requirement stage, leading to misunderstandings. This can result in functionality mismatches, affecting application quality and the organization's credibility.
Poor interaction among project members can create ambiguities, impacting output quality.
Insufficient quality assurance teams may struggle to maintain desired quality due to human resources shortages. Limited resources can lead to exhausting pressure and improper testing, compromising the final product's quality.
Some clients frequently change requirements after module deliveries. Handling changes as enhancements after project delivery is advisable to avoid confusion and ensure timely delivery.
Covering all scenarios in a test document quickly can be challenging. Skilled resources with automation knowledge are crucial to overcome this and deliver a minimal-error product.
Quality assurance professionals must ensure the application works well in the client's production URL. Smart communication with clients is vital to resolving issues, as functionalities may differ between production URLs and client machines.
Utilizing advanced automation tools for efficient and fast testing is essential. However, a significant challenge lies in finding a skilled automation tester for the project who can perform testing intelligently, aiming for maximum customer satisfaction.
Identifying the right tester, one who is knowledgeable about automation tools and programming languages, is equally crucial for enhancing the product. Automation frameworks enable quick testing, allowing for quick validation even with minor bug fixes when running scripts on modern tools.
Speed and quality are essential in developing a project. Assigning a sufficient team with dedicated resources for testing ensures a fast process without compromising on important scenarios, avoiding quality lags in the final deliverable.
Techniques to Overcome Quality Assurance Testing Challenges
The Quality assurance testing team can use specific strategies or techniques to achieve project goals despite challenges. Following these strategies or techniques below can be beneficial, enabling the quality assurance team to deliver high-quality products to end users consistently.
- Clear Requirements and Priorities
- Improved Communication and Collaboration
- Efficient Resource Allocation
- Continuous Testing Implementation
The quality assurance team should carefully understand and clarify project requirements with clients to avoid confusion. Confirm expectations with clients, promptly address unclear documents, and establish module delivery priorities.
Quality assurance members should communicate effectively within the project team, sharing information for better project focus. Collaborate with stakeholders to understand project expectations and align efforts to meet them.
Efficiently manage resources in testing, where each tester takes ownership of assigned modules. Testers should ensure error-free modules, with one tester handling integration testing. Assigning testers for regression, retesting, smoke, usability, and compatibility contributes to product quality.
Implement rigorous testing after each error fix to contribute to a quality deliverable. Testers should proactively manage the number of bugs fixed, distribute them among the team, ensure that a single bug fix does not impact other modules, and ensure all functionalities are working well.
Future of Quality Assurance
Quality assurance evolves with technological advancements. It involves the integration of cutting-edge technologies like Artificial Intelligence(AI), Machine Learning (ML), cloud computing, and more.
AI and ML in QA
AI and ML are transforming quality assurance practices. They contribute to intelligent test generation, predictive analytics, and anomaly detection. These technologies enhance test coverage, identify potential defects, and optimize test execution. ML algorithms analyze large datasets to identify patterns, enabling data-driven decision-making for improved quality assurance processes.
Shift-Left Testing
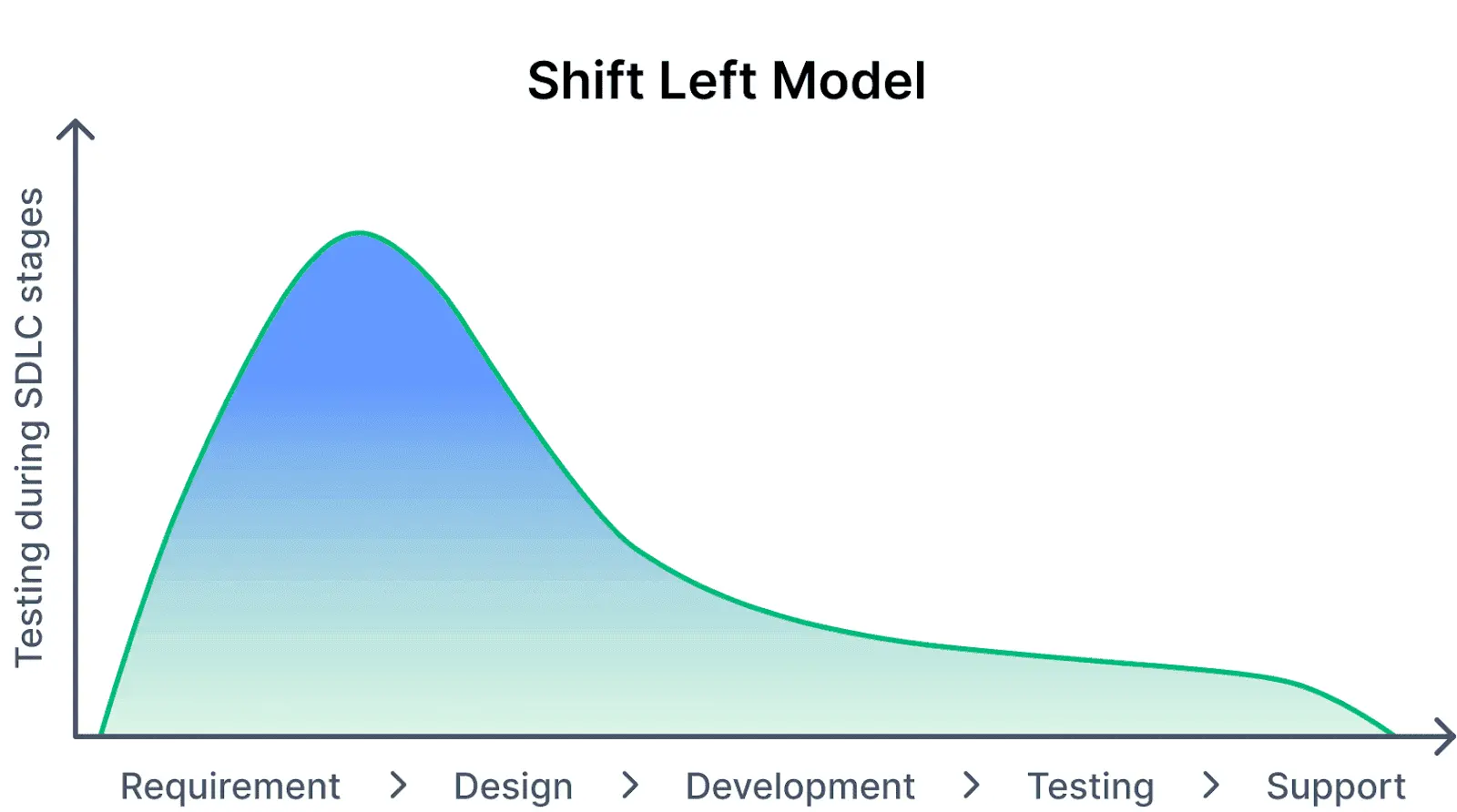
Shift-Left Testing emphasizes early quality assurance involvement in the software development lifecycle. By initiating testing activities during requirements gathering and design phases, potential issues can be identified and resolved early, reducing rework and enhancing overall quality.
Quality Assurance in Cloud and Mobile Computing
he rise of cloud computing and mobile applications requires adapting QA practices. Testing on various devices, screen sizes, and network conditions becomes crucial. QA professionals must consider scalability, security, performance, and compatibility in cloud and mobile computing environments.
Security Testing and QA
As cybersecurity threats evolve, integrating security testing into quality assurance processes is crucial. Security testing identifies vulnerabilities, safeguards sensitive data, and protects systems from attacks. Techniques like penetration testing, vulnerability scanning, and secure coding practices ensure robust security in software applications.
Virtual and Augmented Reality Testing
The emergence of virtual reality (VR) and augmented reality (AR) technologies presents new challenges to QA. Testing user experiences, interaction interfaces, and performance in VR and AR environments require specialized testing techniques. QA teams must adapt and develop strategies to ensure quality in these immersive and interactive applications.
Now that we know the quality assurance testing challenge and strategy to overcome the challenges and its future let us explore some of the best practices in quality assurance testing below.
Best Practices of Quality Assurance Testing
Implementing these quality assurance best practices can help you achieve the highest product delivery standards.
- Combine Manual and Automated Testing.
- Utilize Crowd Testing
- Implement Continuous Integration and Delivery Testing
- Include Risk Management.
- Achieve Quality with Speed
- Ensure Effective Methodologies
- Conduct Continuous Monitoring
- Utilize Analytics
- Cover Multiple Exigencies
- Implement Regression Testing
Achieve optimal QA testing results by combining manual and automated testing. Manual testing covers many scenarios, while repetitive tests benefit from automation. Use automation as a supplement to manual testing.
Improve testing scalability by leveraging crowd-testing. Engage a large population of QA testers simultaneously, allowing cross-browser testing on various operating systems, and diverse software compatibility. Combine in-house testing, crowd testing, and automated testing for optimal results.
Using continuous integration to update small code sections into a central module, running test scripts with each code update. Continuous delivery and integration testing enable periodic releases, efficiently addressing user experience issues.
Integrate risk management into QA testing processes to control and address potential problems. This enhances QA activities and ensures a high-quality final product.
Regularly review QA process efficiency throughout the product development cycle. Aim for high-quality outcomes by testing unit code during development, employing continuous integration and delivery (CI/CD), and conducting parallel testing.
Lower product development costs by implementing effective software QA testing processes that align with requirements and guidelines.
Maintain adherence to relevant standards and procedures throughout the development process by continuously monitoring QA test practices.
Leverage predictive analytics to anticipate potential bug locations based on past test data. Utilize various types of data, including defect data, testing-related data, development data, application data, operation data, and customer usage data.
Use QA testing methodologies to encompass various conditions and scenarios, including different devices, operating systems, and user profiles.
Address potential errors in previously passed features due to new code additions by implementing a robust regression testing system.
Conclusion
Understanding the fundamental principles of quality assurance, including continuous improvement, adopting a user-centric approach, effective risk management, implementation of standardized processes, and making evidence-based decisions, serves as a guiding framework to achieve customer-centric excellence. Moreover, quality assurance encompasses crucial components such as quality planning, quality control, documentation, competence and training, collective and preventive steps, review and auditing, consistent and continuous improvement, and QA metrics and reporting.
In addition to these foundational elements, exploring QA tools and addressing associated challenges equips us with valuable insights. Strategies for overcoming challenges are vital, accompanied by best practices to ensure effective quality assurance. Furthermore, anticipating the future of QA testing involves staying abreast of emerging trends, adopting innovative strategies, and integrating cutting-edge technologies.
This comprehensive understanding of key principles, components, tools, challenges, and prospects in QA testing positions businesses to consistently deliver high-quality products or services, fostering customer satisfaction and long-term success.
On this page
- Overview
- What is Quality?
- What is Quality Control?
- What is Quality Assurance (QA)?
- Difference between Quality Control and Quality Assurance
- Key Principles of Quality Assurance
- Quality Assurance Components
- How to Carry Out Quality Assurance?
- Main Stages in the QA Process
- Why Should QA Processes Be Implemented?
- Types of Quality Assurance Testing (Manual & Automation)
- Tools Required for Quality Assurance Testing
- Quality Assurance Challenges in Testing
- Techniques to Overcome Quality Assurance Testing Challenges
- Future of Quality Assurance
- Best Practices of Quality Assurance Testing
- Conclusion
- Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Frequently asked questions
- General
Author's Profile

Saniya Gazala
Saniya Gazala is a Computer Science graduate from Reva University. She began as a manual tester, honing her skills in defect identification and problem-solving. Transitioning to technical writing, she simplified complex tech concepts for users. Her journey is marked by continuous learning and growth in the tech industry.
Reviewer's Profile

Shahzeb Hoda
Shahzeb currently holds the position of Senior Product Marketing Manager at LambdaTest and brings a wealth of experience spanning over a decade in Quality Engineering, Security, and E-Learning domains. Over the course of his 3-year tenure at LambdaTest, he actively contributes to the review process of blogs, learning hubs, and product updates. With a Master's degree (M.Tech) in Computer Science and a seasoned expert in the technology domain, he possesses extensive knowledge spanning diverse areas of web development and software testing, including automation testing, DevOps, continuous testing, and beyond.
Did you find this page helpful?
More Hubs
Try LambdaTest Now !!
Get 100 minutes of automation test minutes FREE!!